Robotic cancer treatments depend on the type and stage of the cancer. They may cure it, prevent the cancer from spreading, or relieve symptoms caused by cancer or its surgical treatment. so book an appoinent for the best colon cancer treatment doctor in Faridabad
Overview of The Best Colon Cancer Treatment
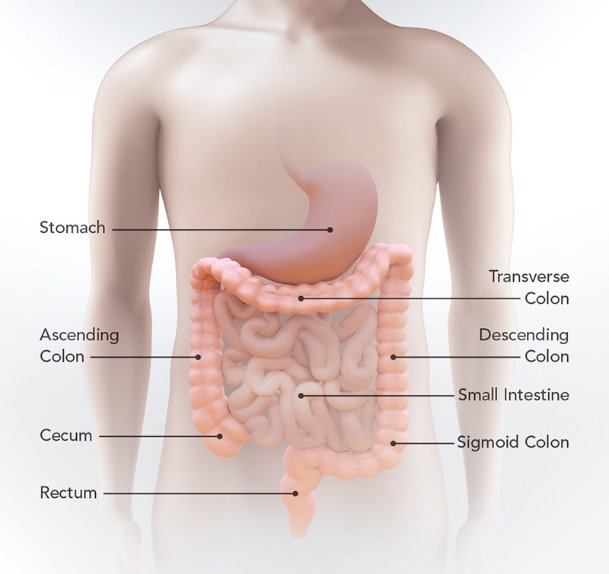
The colon comprises the big intestinal tract or the large bowel. It is the passageway which connects the colon with the anus. If cancer develops in the rectum, or the colon this is known as colorectal cancer.
Colon cancer typically affects older adults, though it can happen at any age. It usually begins as a small, noncancerous (benign) clumps of cells called polyps that form on the innner layer of the colon. Over time some of these polyps can become colon cancers.
Risk factors:
Factors that may increase your risk of colon cancer include:
- Older age: Colon cancer can be diagnosed at any age, but a majority of people with colon cancers are older than 50 years of age. The prevalence of colon cancer among those who are younger than 50 have been growing.
- African-American race: African-Americans are more at chance of developing colon cancer than people from other races.
- A personal history of colorectal cancer or polyps: If you've already had colon cancer or noncancerous colon polyps, you have a greater risk of colon or rectal cancers in the future.
- Inflammatory intestinal conditions: Chronic inflammation of the colon, including Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis may increase your chances of developing colon cancer.
- Inherited syndromes that increase colon cancer risk: Some gene mutations passed through generations of a family can increase the risk of colon cancer significantly. Only a small proportion of colon cancers can be traced to genetic inheritance. The most frequent inherited disorders that can increase the risk of colon cancer are familial polyposis (FAP) along with Lynch syndrome, also referred to as hereditary polyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC).
- A family history of colon cancer: A person is more likely to get colon cancer in the event that a blood relation has suffered from the cancer. When more than one blood relative suffers from rectal or colon cancer, the chance is higher.
- Low-fiber, high-fat diet: Colon cancer as well as rectal cancer might be a result of a common Western diet that is very low in fiber, and also high in calories and fat. The research in this area has yielded mixed outcomes. Certain studies have revealed an higher chance of developing colon cancer in those who consume diets that are rich in red meat as well as processed and cured meats.
- A sedentary lifestyle:An unhealthy lifestyle. Inactive people have a higher risk of developing colon cancer. Regular exercise can decrease your risk of colon cancer.
- Diabetes: Numerous studies have shown that people suffering from insulin resistance or diabetes are at an increase risk developing colon cancer.
- Obesity:Obese people have an increased risk of developing colon cancer, and a higher chance of dying from colon cancer compared to people who are considered to be of normal weight.
- Smoking:Smokers are at risk of an increase risk for developing colon cancer.
- Alcohol:Drinking heavily increases the chance of developing colon cancer.
- Radiation therapy for cancer: The use of radiation therapy targeted at an abdomen area for treatment of prior cancers may increase the chance of developing colon cancer.
A few signs and symptoms of colon cancer comprise:
- An ongoing change in your bowel routine, like constipation, diarrhea or an alteration to the texture of your stool.
- Blood inside your stool.
- Insistent abdominal pain that persists including gas, cramps or discomfort,
- A feeling that your bowel doesn't empty completely.
- Weakness or fatigue.
Diagnosing colon cancer:
- Digital Rectal Examination: By doing digital examination your surgeon can find growth in the lower rectum and anal canal. Punch biopsy can be taken easily from the growth.
- Proctoscopy: By inserting special instrument rectal growth can be seen and biopsy to diagnose cancer can be obtained.
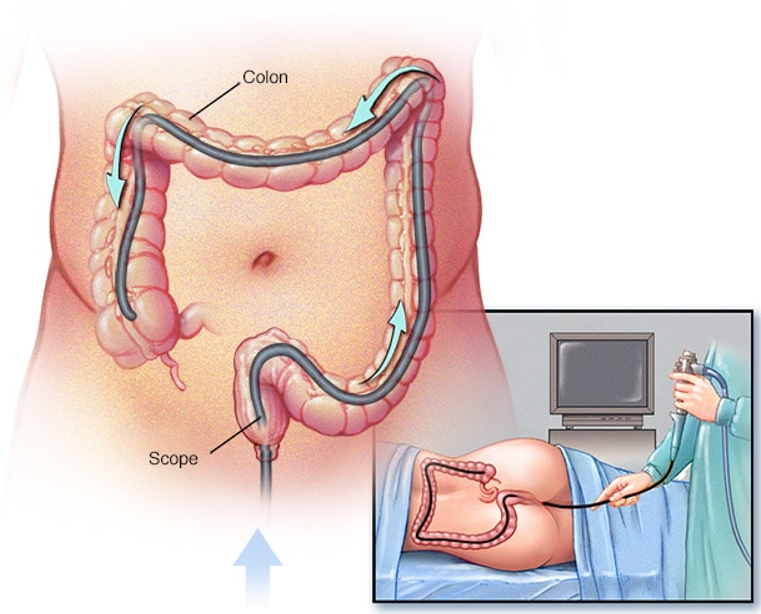
- Colonoscopy.Colonoscopy uses a long, flexible and slender tube attached to a video camera and monitor to view the entire colon and rectum. If any suspicious areas are found, your doctor can pass surgical tools through the tube to take tissue samples (biopsies) for analysis and remove polyps.
- Blood tests.No blood test can tell you if you have colon cancer. But your doctor may test your blood for clues about your overall health, such as kidney and liver function tests.
- CEA:Your doctor may also test your blood for a chemical sometimes produced by colon cancers (carcinoembryonic antigen, or CEA). The time-lapsed amount of CEA in your blood can help your doctor determine your outlook and whether or not your cancer responds to treatment.
- Radiology: If you've been diagnosed with colon cancer, your doctor may recommend tests to determine the extent (stage) of your cancer. Staging helps determine what treatments are most appropriate for you. CT, MRI are routinely done to see the local extent of the disease and PET CT done to see the distant metastatic disease.
Staging:
The Stages of cancer in the colon are outlined by Roman numerals that vary between 0 and IV, with the lowest stage being those that are limited to the lining interior part of the colon. At stage IV when the cancer is diagnosed as stage IV, it's considered advanced and has expanded (metastasized) to other parts within the body.
Screening:
Colorectal cancer is one of the leading cause of cancer death worldwide, but it doesn’t have to be. Colorectal cancer screening saves lives. Screening for precancerous polyps can reveal or abnormal growths that occur in the rectum or colon which can be eliminated before they develop into cancer. Screening is also a way to detect colorectal cancer in its early stage, when treatment is at its most effectively. Doctors typically recommend that those who have a moderate risk of developing colon cancer start screening by age 45. However, people who have an increased risk, like those who have a family history of colon cancer, should think about the screening sooner.
Treatment
Treatment depends upon the stage of the disease, location of the tumor and general condition of the patient. The mainstay of treatment is to remove the cancerous mass. Other treatments include chemotherapy, radiotherapy, targeted therapy and immunotherapy.
Surgery
Surgery generally recommended in early stage disease. It is also done in cases with locoregional disease after neoadjuvant chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Surgery can be done with open technique, laparoscopic technique or robotically. Robotic surgery in colorectal cancers are in many ways better than laparoscopic surgery and equally effective as open procedures.
Surgery for Early stage disease:
1. Polypectomy: If the cancer in the colon or rectum is a small polypoidal mass and localized to it, then removal of the polyp completely can be done while performing colonoscopy and it can be curative.
2. Endoscopic Mucosal Resection: Larger polyp may be removed along with the inner layer of colon and rectum using special instruments and technique called endoscopic mucosal resection.
3. Minimally invasive Surgery: Polyps than can not be removed during colonoscopy can be removed using laparoscopy or Robotic technology. Robotic Surgery now a days becoming standard of care for many of the cases. In minimally invasive procedures, surgeons perform operation through multiple small holes made in the abdomen, inserting instruments in your abdomen, visualizing colorectal area and growth with the help of a camera and performing surgery. Robotic technology can provide high precision 3 D visualization of the surgical field.
Various forms of colectomies can be done depending upon the location of the tumor eg. Right and Left Hemicolectomy, Total Colectomy. Similarly for the Rectal cancers, Anterior resection, low anterion resection, ultra-low anterior resection or Abdomino-pelvic resections can be performed. Robotic technology has got advantage over other procedures in deep pelvis in cases of rectal cancers.
4. Open technique: All these procedures can be performed through open technique also after making an incision in the abdominal wall.
5. Lymphadenectomy: Nearby lymph nodes are also removed during the procedures which may harbor cancerous cells.
Surgery for more advanced disease:
Many patients presents with advanced stage who requires chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy (called Neoadjuvant) before proceding to Surgery. This is to downgrade the tumor. All the above mentioned procedures can be performed after neoadjuvant therapy.
If the stage of the cancer is very advanced, patients general condition is not good and patients presents with obstruction in the bowel, in that case your surgeon may recommend an operation to relieve the blockage called ileostomy or Colostomy. This may help in relieving the symptoms. In thiese situations, surgery is not done to cure the disease but to relieve the patients from obstruction, bleeding or pain.
Surgery in metastatic Setting:
When the cancer has spread to other organs of the body, it is called metastatic disease. In metastatic colorectal cancers, if the patients general condition is good and there is limited numbers of metastatic lesions in Liver or Lungs, your surgeon may offer surgery for the disease with curative intent. In these situations, chemotherapy is generally required before or after the surgery.
Chemotherapy: These are drugs to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy for colon cancer is usually given after surgery if the cancer is larger or has spread to the lymph nodes. In this way, chemotherapy will kill any cancer cells that remain in the body and help reduce the risk of cancer recurrence.
Chemotherapy used before an operation is called neoadjuvant chemotherapy. The intention is to shrink a large tumor so that it can be remove with surgery.
Chemotherapy can also be used to relieve symptoms of colon cancer that can't be removed with surgery or that has spread to other areas of the body. Sometimes it's combined with radiation therapy.
For some people with low-risk stage III colon cancer, a shorter course of chemotherapy after surgery may be possible. This approach may reduce the side effects compared with the traditional course of chemotherapy, and may be just as effective.
Targeted drug therapy:
Targeted drug treatments focus on specific abnormalities present within cancer cells. By blocking these abnormalities, targeted drug treatments can cause cancer cells to die. Targeted drugs are usually combined with chemotherapy. Targeted drugs are typically reserved for people with advanced colon cancer.
Immunotherapy:
It is a drug treatment that uses your immune system to fight cancer. Your body's disease-fighting immune system may not attack your cancer because the cancer cells produce proteins that blind the immune system cells from recognizing the cancer cells. Immunotherapy works by interfering with that process. Immunotherapy is usually reserved for advanced colon cancer. Your doctor might have your cancer cells tested to see if they're likely to respond to this treatment.
Radiotherapy:
Radiation therapy uses powerful energy sources, such as X-rays and photons, to kill cancer cells. It might be used to shrink a large cancer before an operation so that it can be removed more easily. Sometimes it is used after surgical resection of the tumor. When surgery isn't an option, radiation therapy might be used to relieve symptoms, such as pain. So book an appointment now.
Copyright © Dr. Surender Dabas. All rights reserved. Designed by Innovative Digital Marketing