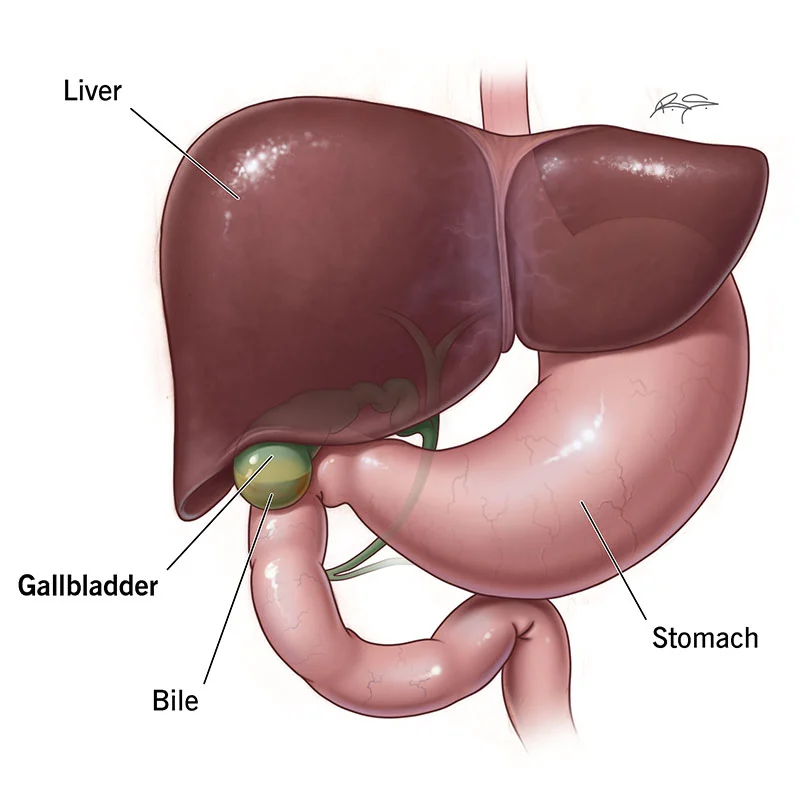
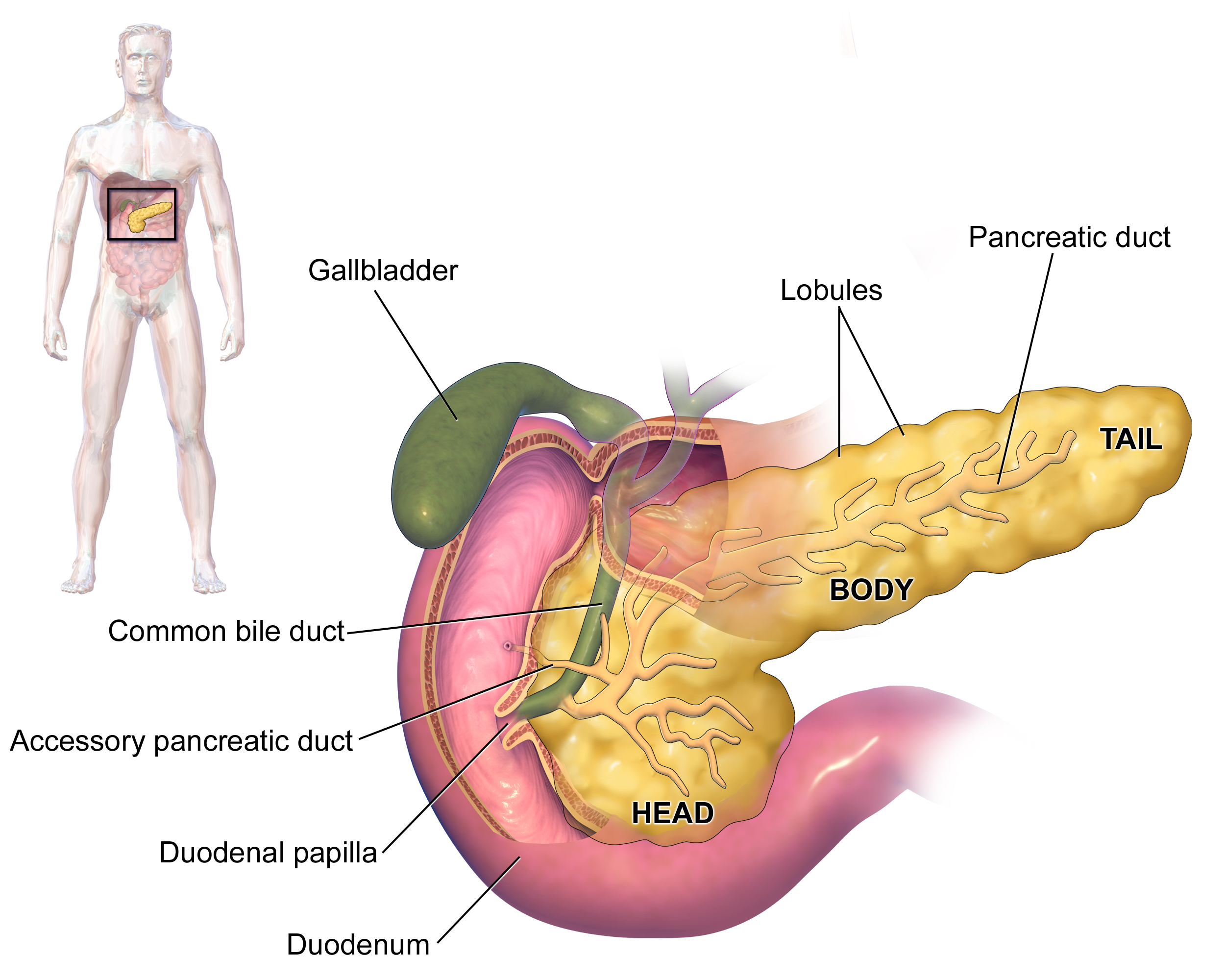
Hepatobiliary cancers are highly lethal. In 2008, approximately 21,370 persons in the United States were estimated to be diagnosed with liver or intrahepatic bile duct cancer and 9520 with gallbladder cancer or other biliary tract cancer. Furthermore, approximately 18,410 deaths from liver or intrahepatic bile duct cancer and 3340 deaths from gallbladder cancer or other biliary tract cancer were estimated to occur.
The types of hepatobiliary cancers covered in these guidelines include hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), gallbladder cancer, intrahepatic cholangio-carcinoma, and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. By definition, these guidelines cannot incorporate all possible clinical variations and are not intended to replace good clinical judgment or individualization of treatments. Although not explicitly stated at every decision point of the guidelines, patient participation in prospective clinical trials is the preferred option for treatment of hepatobiliary cancers.